Esters
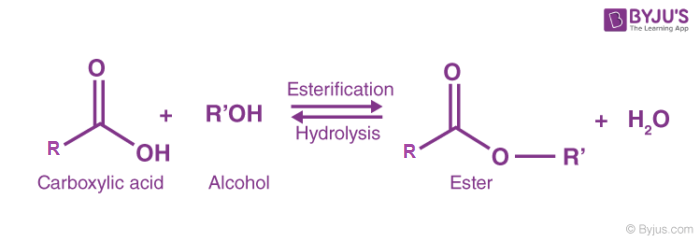
Esters are a group of organic compounds produced when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4). This type of reaction is known as esterification.
During esterification, an ester and water are formed:
Because water is eliminated during the reaction, it is also classified as a condensation reaction.
One of the simplest esters is ethyl ethanoate. Esters are also known as alkanoates and have the general formula: RCOOR', where R and R' are alkyl groups (the hydrocarbon parts).
Structure of Esters
Esters contain a functional group responsible for their chemical properties. In the RCOOR' group:
- R' is an alkyl group derived from the alcohol.
- RCOO− is the carboxylate group derived from the carboxylic acid.
 Credit: Byju
Credit: Byju
Many esters occur naturally and are responsible for the pleasant smells and flavors found in fruits and flowers.
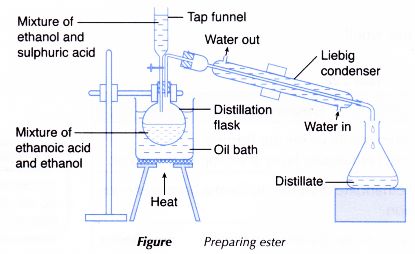
Preparation of Ethyl Ethanoate
Ethyl ethanoate is formed through esterification between ethanol and glacial ethanoic acid at 150°C, in the presence of concentrated tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid (\( H_2SO_4 \)) as a catalyst.
\( C_2H_5OH + CH_3COOH \xrightarrow{H_2SO_4,\,150^\circ C} CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O \)
 Credit: aplustopper
Credit: aplustopper
Physical Properties of Ethyl Ethanoate
- It is a colourless, volatile liquid with a pleasant smell.
- It is slightly soluble in water.
- It has a boiling point of 75°C.
Chemical Properties of Ethyl Ethanoate
1. Hydrolysis
Ethyl ethanoate can be hydrolyzed by water to yield ethanoic acid and ethanol:
\( CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O \rightarrow CH_3COOH + C_2H_5OH \)
Note: If an alkali like sodium hydroxide is used instead of water, the salt of the acid is formed:
\( CH_3COOC_2H_5 + NaOH \rightarrow CH_3COONa + C_2H_5OH \)
2. Reaction with Ammonia
Ethyl ethanoate reacts with ammonia to produce ethanol and ethanamide:
\( CH_3COOC_2H_5 + NH_3 \rightarrow CH_3CONH_2 + C_2H_5OH \)
3. Reduction
Ethyl ethanoate can be reduced using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III) (also known as lithium aluminium hydride, \( LiAlH_4 \)), producing ethanol:
\( CH_3COOC_2H_5 + 4[H] \rightarrow 2C_2H_5OH \)
Uses of Alkanoates (Esters)
- Used as food flavouring agents.
- Used in perfumes and cosmetics.
- Used as solvents for cellulose nitrate.
- Used in quick-drying products like paints and nail varnishes.