Biomes
Biomes are large ecosystems defined by their dominant vegetation. They are considered terrestrial because plants make up most of the community. For instance, forest biomes feature dense, tall trees, while savannas have grasses and scattered shrubs. Factors such as rainfall, humidity, temperature, wind, and sunlight determine the type of vegetation in each biome.
Biomes in Nigeria
Nigeria's diverse climate, topography, and geography support various biomes. Below are the major biomes found in Nigeria:
- Mangrove Swamps: Found along Nigeria’s coastal areas, particularly in Lagos, Delta, Edo, Rivers, Ondo, and Cross River States. These wetlands are home to small evergreen trees with unique roots, like pneumatophores for breathing. The climate is hot and wet, with annual rainfall exceeding 250 cm.
- Tropical Rainforests: Located between the equator and latitudes 5°–10°N, these forests feature diverse trees, climbers, and epiphytes. Rainfall is consistent year-round, and temperatures average 27°C. States like Edo, Delta, Ondo, Lagos, and Rivers host these forests.
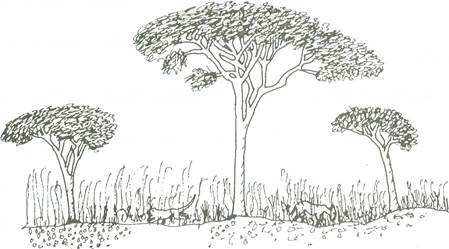
- Savannas: Tropical grasslands with scattered trees and a mix of dry and wet seasons. Annual rainfall ranges from 500 mm in semi-arid areas to 1500 mm near rainforests. Found in Enugu, Kogi, Benue, Kwara, Oyo, Osun, and Ekiti States.
- Northern Guinea Savanna (Sudan Savanna): Characterized by short grasses and scattered thorny trees like acacia and baobab. Rainfall is low, between 50–100 cm annually. Found in states like Kaduna, Bauchi, Niger, and Adamawa.
- Southern Guinea Savanna: Features tall grasses and scattered broadleaf trees like locust bean and shea butter. Annual rainfall ranges from 100–150 cm. Found in Enugu, Kogi, Kwara, Ebonyi, and Ekiti States.
Major Biomes of the World
- Deserts: Dry regions with sparse vegetation, mostly succulents and deep-rooted plants. Rainfall is minimal, and temperatures are extremely high. Examples include the Sahara Desert and Arabian Desert.
- Temperate Grasslands: Open grasslands with moderate rainfall, cold winters, and hot summers. They support grazing animals and birds. Examples include the steppes (Asia), prairies (North America), and pampas (South America).
- Coniferous Forests: Dominated by needle-leaved evergreen trees like pines and firs. These forests are cool with light rain or snow. Found in North America and Eurasia.
- Temperate Shrublands: Composed of drought-resistant shrubs and small trees. Summers are hot and dry, while winters are mild and wet. Found in northeastern Brazil, Australia, and parts of West Africa.
- Mountain Vegetation: Forests grow on mountain slopes, with vegetation becoming sparse at higher altitudes. Afro-alpine vegetation includes heaths and grasses. Found on Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Cameroon, and the Kenyan Highlands.
- Tundra: Treeless regions with mosses, lichens, and small shrubs, located in cold areas like the Arctic Circle and high-altitude zones. These areas have limited species and bare ground.